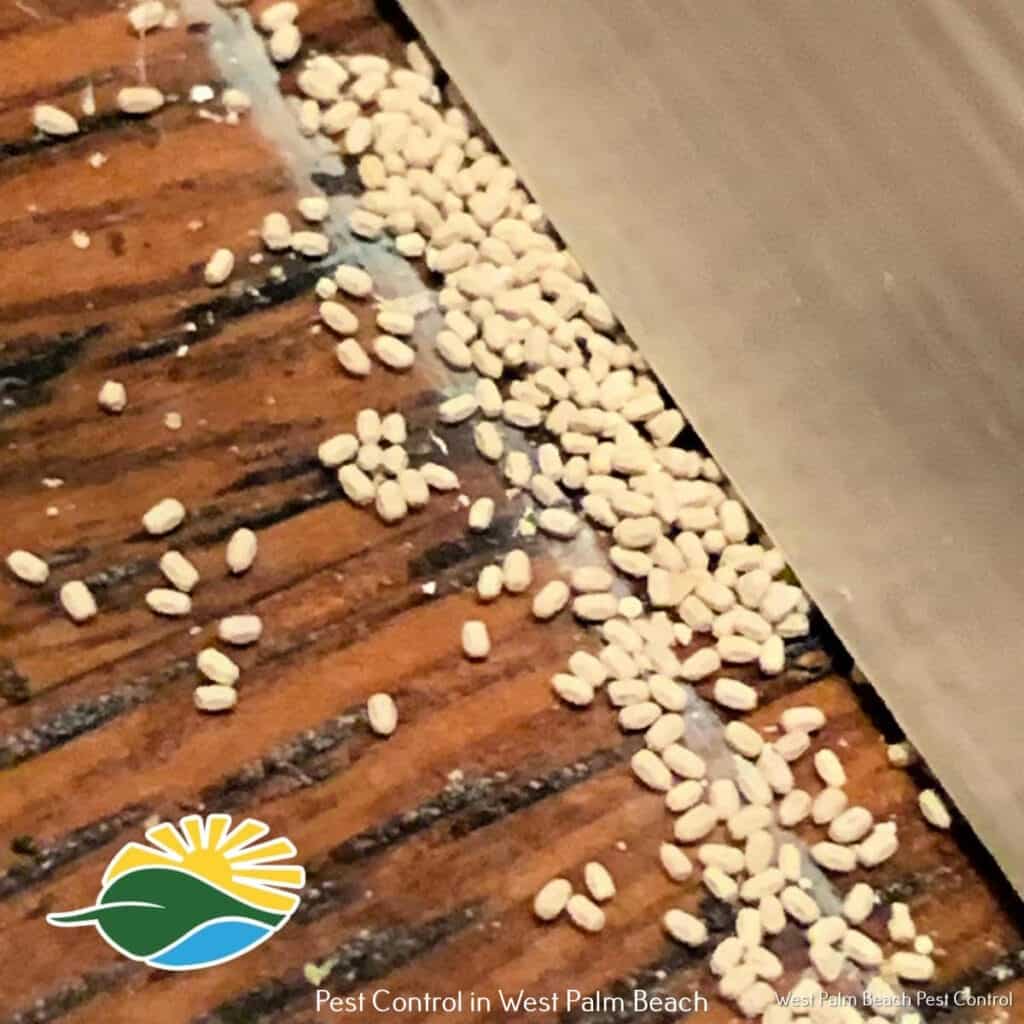
Rust Fungus Information
Appearance:
There are many different types of Rust fungus. Plants that are affected, typically begin with white, sometimes raised, white dots on the underside of the plant’s leaves. The untreated leaves eventually turn orange or red, then yellow and dark. Eventually, the untreated leaves will die and fall off the plant.
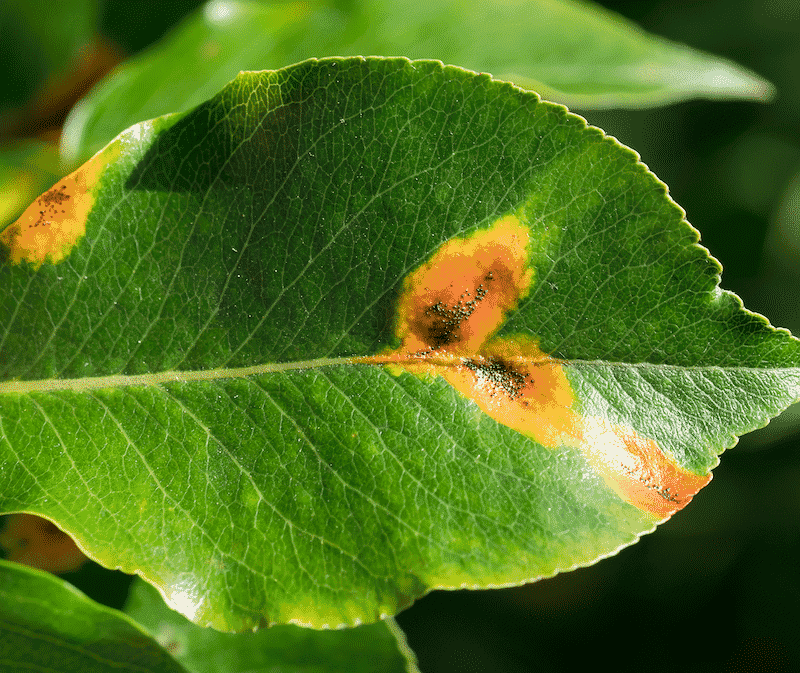

Location and Behavior Patterns:
Once the dead leaves have fallen off of the plant, they should be collected and destroyed or trashed, in order to keep the fungus from spreading to other, healthy leaves. Fungus spores are spread from plant to plant by wind or by water droplets. This fungus is caused by Pucciniales, and it affects many different types of plants, including; roses, daylilies, snapdragons, tomatoes, beans, and lawns. Usually only mature plants are affected, and lower leaves on a plant are usually affected first.
Treatment:
There are a few different ways to treat Rust Fungus. In addition to removing the affected leaves, other things that you can do, in order to prevent this fungus from developing and growing, includes; (1)watering plants early in the day, so they have plenty of time to absorb the needed water, without having a lot of standing water, (2)fertilize the plants so they grow strong and healthy, and (3)prune plants that have an excess of foliage, in order for more air to circulate around the plant. Furthermore, a broad-spectrum fungicide can be used, to help stop the fungus growth on the plant.