Termites are fascinating creatures that play a significant role in our ecosystem, but when they invade our homes or buildings, they can become a nuisance and cause extensive damage. Understanding the lifecycle and characteristics of baby termites is important for effective termite management and environmental control.
So, what do baby termites look like? This article delves into the intricate details of their appearance and learns how to distinguish them from their adult counterparts.
The lifecycle of baby termites
The life cycle of termites is a fascinating process that involves distinct stages of development. From eggs to nymphs and finally, to adult termites, each phase contributes to the growth and survival of termite colonies.
It all begins with the termite queen, who lays eggs within the colony. These eggs are typically small, translucent, and grouped in clusters. The queen’s sole purpose is to reproduce, and she can lay thousands of eggs in her lifetime.
After a period of incubation, the eggs hatch, giving rise to baby termites known as nymphs. Nymphs are tiny, pale in color, and have soft bodies. They undergo several molts as they grow, shedding their exoskeleton and developing into more mature forms.
During their growth, nymphs play essential roles within the termite colony. They contribute to the expansion of the colony’s population and participate in tasks such as nest-building, foraging for food, and caring for other members. Nymphs are responsible for the digestion of cellulose-rich materials, which form a significant part of their diet.
As the nymphs continue to develop, they gradually transform into adult termites. The time it takes for nymphs to reach adulthood varies depending on the termite species and environmental conditions. Once they become adults, termites take on specific roles within the colony, such as workers, soldiers, or reproductive individuals.
It is important to note that baby termites, or nymphs, are crucial for the growth and survival of termite colonies. Their collective efforts contribute to the construction and maintenance of termite nests, the acquisition of food sources, and the continuation of the termite population.
What do baby termites eat?
Baby termites, also known as nymphs, have specific feeding habits that are vital to their growth and development. They primarily feed on cellulose-rich materials, which serve as their main source of nutrients.
Cellulose, a complex carbohydrate found in plant-based materials, forms the major component of the diet for termites. Wood, leaf litter, plant debris, and other organic matter containing cellulose are all potential food sources for baby termites.
These tiny creatures possess specialized enzymes and microorganisms within their digestive systems that enable them to break down cellulose. Through a process called symbiotic digestion, termites can extract nutrients from cellulose that would otherwise be indigestible to most organisms.
The ability of baby termites to efficiently digest cellulose is crucial not only for their individual development but also for the survival of the termite colony as a whole. The consumption of cellulose-rich materials plays a significant role in the decomposition of plant matter and the recycling of nutrients back into the ecosystem.
In addition to their primary diet of cellulose, baby termites may also consume fungi and other organic matter present within their habitat. Some termite species have specific dietary preferences or exhibit selective feeding behaviors based on the availability of food sources in their environment.
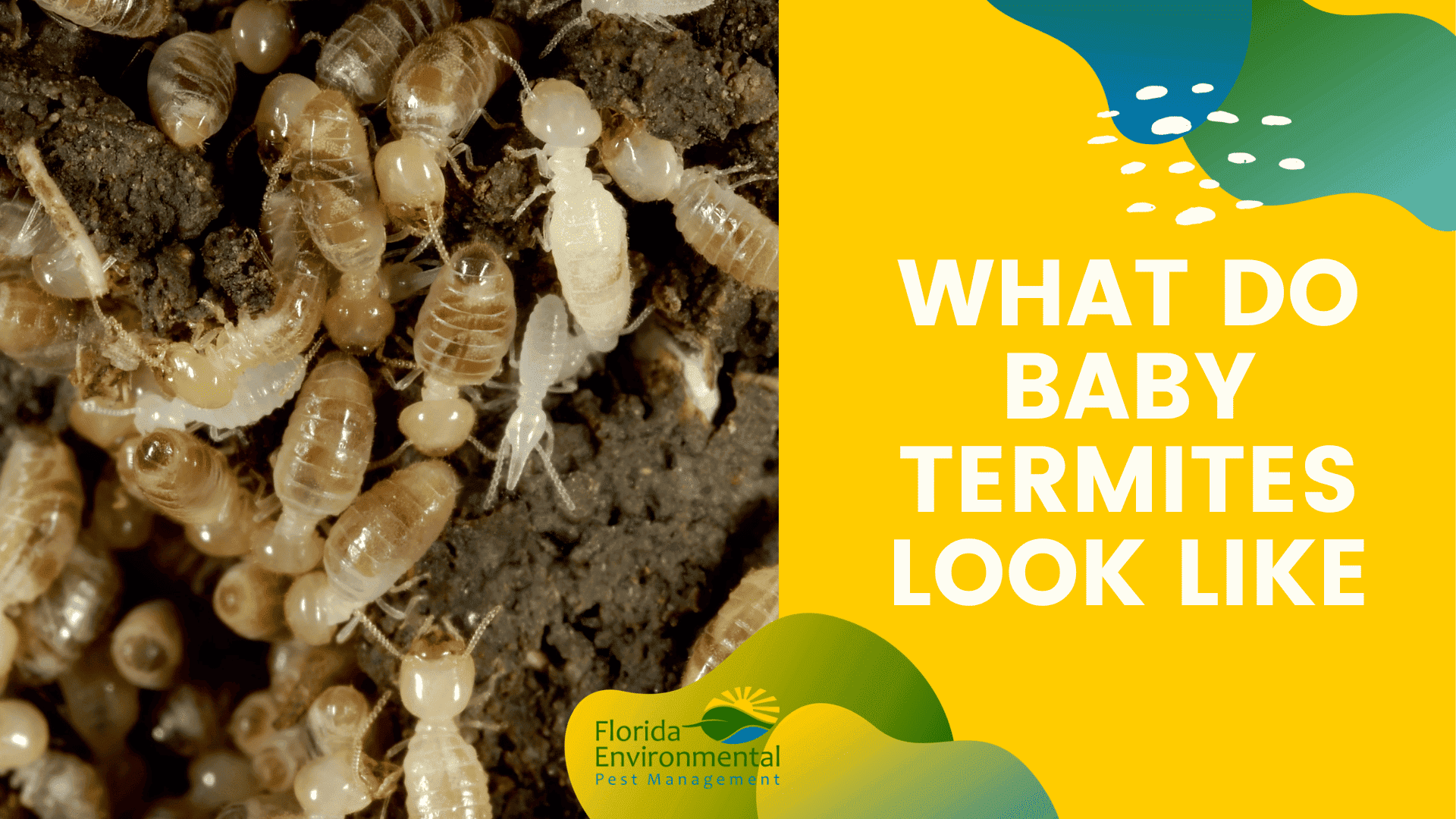
What do baby termites look like?
Baby termites share many physical characteristics with their adult counterparts but exhibit some notable differences. While they resemble miniature versions of adult termites, there are distinct features that set them apart.
1. Size and Color
Baby termites are generally smaller in size compared to their adult counterparts. They measure only a few millimeters in length, depending on the termite species and their specific stage of development. Their small size allows them to navigate through narrow spaces and access food sources within the colony.
In terms of color, baby termites typically have a lighter hue compared to adult termites. Their pale or whitish appearance is due to their soft exoskeleton, which has not yet hardened or darkened as it does in mature termites.
2. Body Structure and Segmentation
Baby termites have a body structure that consists of three main parts: the head, thorax, and abdomen. They possess six legs, just like adult termites, which are used for movement and exploration. These legs are relatively short and delicate, reflecting their small size and early stage of development.
One distinguishing feature of baby termites is their segmented body. The body is divided into distinct sections, providing flexibility and mobility. This segmentation is essential for their coordinated movement and functioning within the termite colony.
3. Soft Bodies and Molting
Baby termites have soft bodies, which is a notable characteristic distinguishing them from adult termites. This softness is due to their exoskeleton being in the process of hardening. As they grow, they undergo a series of molts, shedding their exoskeleton and replacing it with a larger one. Each molt represents a stage of development towards adulthood.
4. Species Variations
It is important to note that the specific physical characteristics of baby termites may vary depending on the termite species. Different species may exhibit slight variations in size, color, and body structure.
However, the key elements of being smaller in size, lighter in color, having a soft body, and possessing six legs and segmented bodies are generally consistent among baby termites.
Do baby termites have wings?
No, baby termites, specifically the nymphs, do not have wings. Baby termites are in an immature stage of development, and their primary focus is on growth and fulfilling colony tasks such as nest-building, foraging, and caring for other members. They do not possess wings during this stage.
As termites progress through their lifecycle, they undergo molts and transition into different castes within the colony. It is during the reproductive stage, when termites become adult reproductives (also known as alates), that wings start to develop.
The alates, often referred to as swarmers, are the reproductive members of the termite colony. They are responsible for leaving the parent colony and establishing new colonies during the mating season. These alates have two pairs of wings, with each wing pair being equal in size.
Nonetheless, it’s important to note that not all termite species produce alates with wings. Some species, like certain subterranean termites, have wingless reproductives. These wingless reproductives, also known as secondary reproductives, develop within the colony and assist in the growth and reproduction of the termite colony.
How do you get rid of baby termites?
Getting rid of baby termites, as well as the entire termite colony, requires a holistic approach that involves both preventive measures and targeted treatments. Here are some effective methods for termite control:
1. Preventive Measures
- Maintain a dry environment. Termites thrive in moist conditions, so it’s important to address any moisture issues in and around your home. Fix leaks, ensure proper drainage, and minimize water accumulation near the foundation.
- Remove moisture sources. Eliminate or reduce potential sources of moisture, such as leaky pipes, clogged gutters, or excessive vegetation near the structure.
- Conduct regular inspections. Regularly inspect your property for signs of termite activity, including mud tubes, damaged wood, discarded wings, or termite droppings (frass). Early detection can help prevent infestations from spreading.
- Avoid wood-to-soil contact. Keep wood materials elevated and away from direct contact with soil. This helps reduce the risk of termite entry into structures.
2. Treatment Options
- Chemical treatments. Professional pest control companies can apply liquid termiticides to the soil around the structure, creating a barrier that repels or kills termites. These treatments can provide long-term protection against termite infestations.
- Baiting systems. Termite baiting systems involve strategically placing bait stations in the ground around the property. The bait contains substances that termites feed on and carry back to the colony, effectively eliminating the entire colony over time.
- Seeking professional help. If you have a termite infestation, it is highly recommended to seek professional assistance. Pest control experts have the knowledge, experience, and specialized tools to effectively identify and treat termite infestations.
3. Structural repairs
- After eliminating the termite infestation, it is essential to repair any structural damage caused by the termites. Replace or repair damaged wood, seal entry points, and reinforce vulnerable areas to prevent future infestations.
It’s important to note that termite control can be a complex process, and the most effective approach may vary depending on the extent of the infestation, termite species, and local conditions. Consulting with a professional pest control company is often the best course of action to ensure proper identification, treatment, and long-term termite control.
Discover Effective Termite Control Solutions for Your Home
If you’ve discovered baby termites in your Florida home, dealing with these destructive pests can be a frustrating experience. However, there’s no need to worry because Florida Environmental Pest Management is here to help.
At Florida Environmental Pest Management, we understand the importance of environmentally friendly pest control methods. That’s why we offer affordable and eco-conscious solutions that are safe for both your family and the environment.
Once we have successfully eliminated the termite infestation, our commitment doesn’t end there. We go the extra mile by routinely monitoring your premises to ensure that your home remains termite-free.
Take the first step towards a termite-free home and enjoy the peace of mind you deserve with Florida Environmental Pest Management. Contact us today to schedule a consultation with our experienced team.